If a spasm in the knee joint is heard during movement, it is the first sign of gonarthrosis. Conservative methods of traditional and alternative medicine will help destroy cartilage and maintain normal motor function. Treatment should begin immediately - only in this case give a favorable prognosis rheumatologists.
What is gonarthrosis?
Inflammatory, degenerative-dystrophic disease that affects the largest joint, the knee, is called gonarthrosis. Quite an unusual medical definition, has a simpler "folk" concept - "salt deposition". However, the clinical picture of joint gonarthrosis has little in common with the excess of calcified salts in the knee joint. They have no effect on the pathology and represent a metabolic side effect of the disorder.
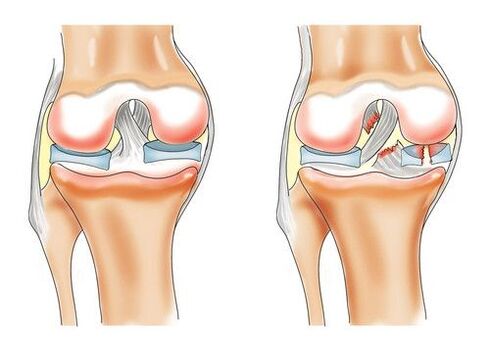
The development of gonarthrosis of the knee joint is facilitated by negative processes in the hyaline cartilage, primarily poor blood circulation in the small bone vessels. Lack of nutrients and oxygen transported by the lymph flow leads to the destruction of the outer cartilaginous layer of the knee.
In the early stages, the disease is very difficult to diagnose. Joint deformation occurs slowly until vitreous hyaline cartilage is considered in the process. The anatomical structure of the ligaments has changed. There is turbidity, the fabric thickens, thins, cracks in all directions. The result of pathology can be complete disappearance of cartilage, leading to neoplasms of bone tissue and irreversible curvature of the knee.
Classification of the disease
The International Classification of Diseases divides gonarthrosis into seven distinct subheadings:
- Bilateral primary gonarthrosis. The diagnosis is most often made by women aged 70 to 74 years and men aged 60 to 64 years. This puts the disease in the category of "elderly".
- Another primary gonarthrosis. Pathology of one knee joint, on the background of natural wear and tear or other diseases.
- Posttraumatic gonarthrosis bilateral. People of different age groups were affected by serious leg injuries.
- Other posttraumatic gonarthrosis. Unilateral, amid limb injuries and bruises.
- Other secondary gonarthrosis is bilateral. They are the result of chronic, not completely cured bruises, fractures or dislocations. Most often it is diagnosed in athletes who have a heavy load on both feet - players, athletes, skaters.
- Other secondary gonarthrosis. Unilateral development of profession-related pathology. For example, miners, metallurgists, fishermen.
- Gonarthrosis, unspecified. Diagnosed with unexplained etiology of the disease, excluding age, occupational and genetic predisposition.
According to medical statistics, more than 10 million people of different age groups suffer from this or that type of gonarthrosis. About 3, 000 people die each year from an established diagnosis.
ᲛReasons
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint develops due to a disturbance of metabolism in the knee joint, which leads to loss of cartilage softness and elasticity.
Destructive processes are caused by various reasons:
- Diseases of the thyroid gland that disrupt the hormonal background;
- Decreased permeability of blood vessels in the knee joint;
- Genetic conditioning;
- Natural aging;
- Past or present knee injuries, of various origins;
- Obesity (more than 20% of the norm), which puts a lot of pressure on the knee joint;
- Inflammatory diseases of the joints (polyarthritis, purulent arthrosis);
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis);
- Specific infectious pathologies (syphilis, tuberculosis, encephalitis);
- Living in ecologically unfavorable areas, poor quality food and water.
Also, rheumatologists identify several additional causes that lead to the development of gonarthrosis. Dysplasia in newborns. With this diagnosis the joint wears out faster. Changes in the structure of collagen lead to disruption of the protein in the connective tissue.
Symptoms depend on the degree of gonarthrosis
Diagnosing the initial stage of knee osteoarthritis is difficult. Only the description of the symptoms by the patients themselves and the external examinations of the rheumatologists provide a clinical picture that differs according to each degree of progression of gonarthrosis:
- I degree gonarthrosis.Attraction of knee pain, feeling of some stiffness, partial loss of sensation, difficulty in bending the leg, especially after prolonged immobility, inability to walk or run for a long time, the appearance of slight swelling. Usually the symptoms disappear after rest or simple anesthesia.
- Grade II gonarthrosis.At this stage it is already possible to determine the pathology on X-ray examination. The pain intensifies and appears after each physical activity. Removal of discomfort is still possible with rest. In the morning it becomes more difficult to straighten the legs, it takes some time to restore motor function. Discomfort is accompanied by frequent cramps in the calf, especially at night. Crutches are heard during movement. Swelling of the knee joint is pronounced. Signs of limb deformity are noticeable.
- Grade III gonarthrosis.There are irreversible changes in the knee joint. Cartilage abnormalities can undoubtedly be detected on X-ray. Knee pain becomes constant, sharp. The leg stops bending at the knee. The patient can not walk without a cane or canes. Swelling is important. The anatomical shape of the knee is smoothed and acquires a firm look. There is a primary curvature of the spinal column.
Diagnosis
A combination of clinical manifestations of knee joint arthrosis and patient complaints is used to make a correct diagnosis. In order to find out or rule out the causes of the disease, studies are conducted in different ways.
The standard diagnosis is as follows:
- Compilation of disease history. History of concomitant diseases, genetic predisposition, past traumas and surgical interventions, professional activities, etc. Sh.
- External evaluation of muscular system deformities. Walking, posture, knee joint condition, leg curvature.
- General inspection. Palpation of the lower leg, thigh, injured joint, determination of the localization of the disease.
- Laboratory tests. A general blood test gives data on the absence of an inflammatory process. If the process takes place against the background of other diseases, then there is an increased rate of erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the blood. Protein, globulin and fibrinogen levels differ from normal values. The biochemical composition will remain within the standard limits. If the progression of the pathology is in the final stage, then a biopsy of the synovial fluid of the knee joint is performed.
- Instrumental research. X-ray is the main and most common method of diagnosing suspected gonarthrosis. Typically, a rheumatologist can easily identify changes in the structure of bone tissue from a picture already at the beginning of stage 2 disease. The presence of lateral diseases and their causes are diagnosed with the help of more modern and accurate equipment - MRI, CT, ultrasound, osteostintigraphy, thermography.
Treatment of gonarthrosis
Like all diseases of the joints, gonarthrosis requires systemic treatment, which is preferable to start at the first symptoms. In this case the prognosis of therapy becomes favorable and ensures a return to a normal lifestyle in a fairly short time.
Comprehensive treatment aims to eliminate the main signs of the disease:
- Discomfort, pain syndrome, and muscle tone;
- Improving the motor function of the knee joint;
- Stopping the cartilage destruction process;
- Strengthening connective muscles;
- Restoration of normal blood circulation in the knee joint.
Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs
They help to cope with pain, relieve swelling caused by inflammation of muscle tissue.
Chondroprotectors
Cartilage tissue regeneration and recovery is impossible without chondroprotectors. They are a major component of conservative treatment.
Vasodilators
They are used to improve intra-articular permeability.
Hormonal drugs
Reduces the production of the hormone cortisone to prevent the development of inflammatory processes.
Hyaluronic acid injections
Used to restore intra-articular synovial fluid. This reduces friction between the joint parts, normalizes motor function, and restores cartilage tissue elasticity.
Anti-enzyme agents
They inhibit the action of trypsin, thus preventing further destruction of the joint. Appointed in the complex.
Physiotherapy
Physiological treatment has been used successfully for decades to treat osteoarthritis of the knee. This can be as a separate type of therapy, for prevention or during the rehabilitation period. Such is the integrated approach to disease.
Most often, the following types of procedures are prescribed by a rheumatologist:
- Electrophoresis with analgesics;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Laser exposure;
- Paraffin applications;
- Mud treatment;
- Therapeutic exercise (exercise therapy);
- Manual therapy, massage with healing ointments.
Surgery and prosthetics
If gonarthrosis is in an advanced stage, the knee joint and cartilage tissues are destroyed, it is impossible to do without surgery. Otherwise, the person will remain viable.
Modern medicine offers several ways to solve the problem:
- Arthrodesis. Complete removal of affected tissues and knee joint. The body is freed from the focus of the disease, but the motor function of the limb is completely lost. It is used extremely rarely if the patient has diseases of the extra joints.
- Arthroscopy. The destroyed hyaline cartilage is removed. The operation is low-trauma, has a short rehabilitation period. It is indicated for patients whose progression has not affected the knee joint itself.
- Periarticular osteoma. A complex operation, the essence of which is to insert deformed bones and a rash, with further connection to the necessary anatomical structure.
- Endoprosthesis. The completely destroyed knee joint is removed and a titanium prosthesis is placed in its place. An effective method that allows you to forget about gonarthrosis forever. Requires careful preparation and long-term rehabilitation.
Traditional medicine
The use of folk recipes in combination with conservative treatment can alleviate external symptoms (pain, swelling). Recipes based on bay leaf, burdock root, St. John’s wort, malt and hay are well proven. Ointments, creams, tinctures and decoctions are made from them.
These plants have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. To achieve a visible result requires regular and long-term use.
Honey-based ointments and compresses, with the addition of alcohol or apple cider vinegar, well relieve swelling and have a calming effect on damaged tissues.
A food mixture is made from lemon and garlic, which is taken orally, one teaspoon after breakfast and dinner. Such a recipe has a general strengthening effect on the body, increases the permeability of blood vessels and nourishes the joints with useful micronutrients.
We must remember that home treatment does not solve the main problem - the pathological destruction of the knee joint.

Diet
Adherence to diet is an integral part of complex treatment. Adjusting your diet will not only help you lose weight, but also provide your bones and joints with essential vitamins.
Contraindicated for a patient diagnosed with gonarthrosis:
- Fried, spicy, salty, pickled foods;
- Fatty broths;
- Sweet cakes;
- Fruits, with high content of acidic enzymes;
- ᲐAlcoholic beverages.
The menu should be filled with raw vegetables, fruits and herbs, low-fat dairy products, bone broths and gelatin-containing dishes (jellies, jellies).
Additional methods
For the treatment of gonarthrosis it is necessary to undergo spa treatment regularly, at least once a year, if possible, more often. Hydrotherapy, mud therapy, and manual therapy procedures can keep the disease going for a long time and prevent joint destruction.
Keeping a sore knee in a stable position will take a lifetime. But it can become quite beneficial for the body as a whole. Reviewing food, eliminating bad habits, playing sports, visiting resorts - the quality of life can be significantly improved.
We must remember that self-medication, ignoring the primary symptoms, and unbearable stress on a sore knee joint can very quickly turn a healthy person into a helpless disabled person.